Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) affects the blood vessels outside the heart and the brain, mainly those in the arms and legs. However, when this condition remains untreated, it can have a severe influence on your lifestyle and quality of life. Fortunately, there are different treatment methods for you to manage this condition successfully. Preventive measures and lifestyle adjustments, on the other hand, have been very useful in reducing PVD. Positive lifestyle changes reduce the risk of having this kind of disease. This guide will deal with the treatment, prevention, and management of peripheral vascular disease comprehensively.
Treatment Options for Peripheral Vascular Disease
Medication

Drugs play basic role in control of PVD and clinical conditions as well as symptoms. Let’s explore the various types of drugs commonly prescribed for PVD:
Antiplatelet Agents
Platelet inhibitors, like aspirin and clogidrele, are given to patients to make it impossible for the blood to clot in arteries that are narrowed down. The medications decrease the chance of a clot formation within the blood vessels by inhibiting platelet aggregation. This continues proper blood flow from important organs and specific body parts to the brain, thereby avoiding heart attack or stroke as a complication.
Cholesterol-Lowering Drugs
The first prescription drug a doctor would most likely give out is a statin. This is the drug that will help to lower the cholesterol numbers to normal levels. It should be mentioned that they are capable of lowering the amount of plaque in the arteries or the accumulation of cholesterol and other substances in these vessels. The reason behind that is their ability to reduce the cholesterol output of the liver as well as the enhancement of its capability to eliminate bad cholesterol from the blood. It helps in inhibiting the development of formation atherosclerosis that is responsible for most of the vascular diseases.
Blood Pressure Medications
A high blood pressure (hypertension) is frequently a result of many other comorbidities, for instance, the peripheral arterial disease. Antihypertensive agents e.g. ACE inhibitors or beta-blockers will be used to reduce blood pressure and also this will relieve the straining of the blood vessels. In an aspect of the reduced blood vessel diameter, the medicine will go on effecting the heart pumping force by which the blood forced would flow more easily and the work load would be relieved.
Medications for Symptom Relief
If a patient is suffering from peripheral artery disease and discomfort/pain, a medical practitioner might suggest NSAIDs. These drugs reduce the leg pain and discomfort thus the overall quality of life and mobility.
While it is true that treatment strategy for peripheral vascular disease should be customized to the particular circumstances of the individual and his/her medical history the common points should primarily concern prevention of disease complications and improving the quality of life. Frequent tests and perpetual reviews are vital to ensure that medications are working well and to adjust a treatment plan accordingly.
Therapy

Besides the medications, there are also some other therapies which can be used to control peripheral vascular disease (PVD). Let’s explore these therapies in detail:
Exercise Therapy
Exercise therapy incorporates physical activities aimed at improving circulation, increasing walking distance, and alleviating symptoms such as leg pain. Simple activities like walking or stationary cycling, which should be prescribed by a doctor, can also aid individuals with PVD in recovery. These activities strengthen muscles, improve blood circulation, and enhance the cardiovascular system.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapists play a significant part in PVD management by ensuring patients are provided with personalized exercises tailored to their individual requirements. As a result, these exercises involve a workout plan aimed at building leg muscles, increasing flexibility, and promoting mobility. Personalized rehabilitation programs are designed by physical therapy to help people with PVD recover their function, decrease pain, and in general improve their quality of life.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapists specialize in helping individuals with PVD adapt to daily activities and maintain independence. Additionally, they provide techniques for saving energy, streamline motion, and avoid falls. An occupational therapist may offer to modify the home environment, educate ways of saving energy, and provide assistive devices to improve functional abilities.
These therapeutic interventions are not only accompanied by medication management and lifestyle modifications, but they form a comprehensive regime for the management of PVD. Through involvement of exercise, physical, and occupational therapy in the treatment plans the people with PVD can experience better vascular health, higher mobility levels and improved quality of life.
Deciding on Surgery

The decision to undergo surgery is significant and depends on several factors:
Severity of symptoms
In most severe cases when the problem becomes too complicated, doctors prefer surgery. The patient’s life becomes unbearable, prompting this course of action.
Location of blockage
The location of the vascular obstruction will influence which type of surgery is performed.
Overall health
In this regard, findings from the examination such as the severity of disease and the general condition of the patient will also be the determining factor on whether surgery is the treatment option.
Surgical Treatment Options for Peripheral Vascular Disease

Doctors tailor non-operative remedies such as drugs or therapy when they fail to alleviate the signs and symptoms of PVD. Such a situation would warrant surgery, given that surgery will allow a patient to regain normal blood flow and therefore to remove these symptoms. Let’s explore the surgical options available in more detail:
1. Angioplasty
Doctors consider angioplasty a highly effective method for opening blocked or narrowed arteries. Typically, doctors use the smallest balloon, located at the end of a catheter, as the tool. Doctors insert the balloon into the affected blood vessel and expand it at the narrowed area, pushing the plaque to the sides of the artery. This widens the blood vessel and eliminates the constriction effectively. This is the angioplasty that opens up the blood vessels to promote blood flow and thereby reducing the symptoms that include leg pain.
2. Stenting
Stenting is normally done in combination with angioplasty. When the balloon has the artery widely opened, a stent—a little metal tube with a mesh—is put into it to keep it open. The stent functions just like a wire mesh, thus providing additional support. This helps maintain artery walls in place and prevents them from being pinched again.
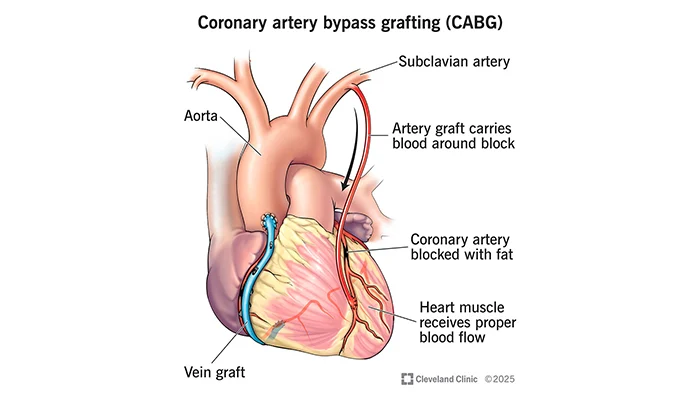
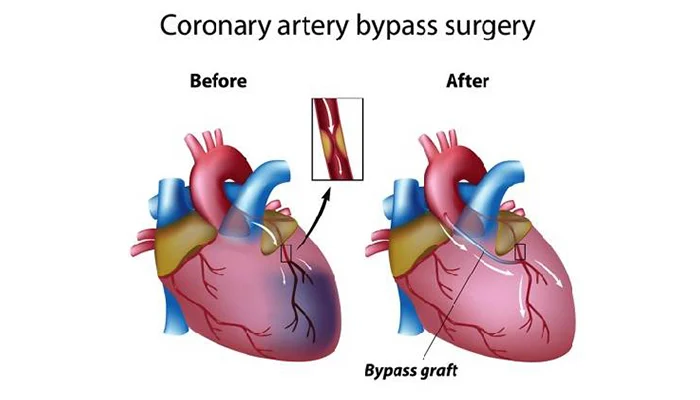
3. Bypass Surgery
Bypass surgery is for those cases when several arteries are blocked or when angioplasty and stenting won’t work. The patient undergoes this surgery using a healthy blood vessel from somewhere else in the body, such as the leg or chest. In bypass surgery, surgeons circumvent the clogged section by using another vessel, ensuring adequate blood flow to the necessary tissue. This redirects blood flow around the blockage, effectively supplying the required oxygen and nutrients.
4. Atherectomy
Atherectomy is the method applied to remove plaque from the arterial walls. Using a thin tube called a catheter with a unique tool or laser at its end, doctors insert it into the artery. This procedure eliminates or burns plaque from the artery, resulting in improved blood flow. Consequently, this action enhances blood flow and alleviates symptoms caused by artery obstructions.
Surgeons use these surgeries to lessen symptoms, ease blood flow, and lower the risk of complications from peripheral vascular disease. Your doctor will determine a particular procedure based on your body’s condition and overall health status.
Possible Complications of Surgery
In patients having treatments, including procedures for PVD, surgical intervention entails certain risks and complications. Here are some of the possible issues:
1. Infection
Even though infections after surgery are rare, there is still a possibility of getting some. Though this problem remains, the medical community has developed protocols, from sterilization methods of surgical instruments to antibiotics, mitigating this risk. Antibiotics, the usual means of treatment, can tackle the infection effectively.
2. Bleeding
Some bleeding is usually normal after surgery, but if it is too much, it may call for medical attention. Surgeons have to take a very careful approach to avoiding or reducing early or late bleeding; however, they may need to intervene much more when massive bleeding occurs.
3. Blood Clots
Operation may be accompanied by the development of blood clots in the legs or another widespread system, respectively. A dislodged clot can cause a blockage of the lung if it travels to the lung. This can cause death if precautions are not taken. One of the ways to minimize this risk will be through patients getting anticoagulants and encouraging them to get as active as possible as soon as the procedure is over.
4. Re-blockage
The treated artery may narrow or become blocked again despite successful surgical intervention. This can happen due to the progression of the existing vascular disease or the creation of new plaque. The key to the condition is to have regular check-ups with the healthcare providers to monitor the symptoms and take any action needed to address the recurrence of symptoms.
Prevention and Lifestyle Adjustments

1. Quit Smoking
Smoking raised the occurrence rate of PVD (peripheral vascular disease) many times, consequently damaging blood vessels. Ceasing the smoking habit disallows the plaque to rapidly cease up the arteries, therefore swerving the chance of complications such as heart attack and stroke.
2. Maintain a Healthy Diet
Eating a balanced diet low in unhealthy fats, cholesterol, and salt helps manage cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Consequently, this reduces the risk of developing PVD and maintains the health of your heart and blood vessels.
3. Stay Active
The effectiveness of exercise in cardio-vascular health is beyond any doubt and you should take exercises in order to retain your fitness. Be sure to perform at least 30 minutes of moderate intensity activity like brisk walking or swimming most of the week. Older people are encouraged to engage in physical activity as they improve blood circulation and heart health thus eliminating peripheral vascular disease.
4. Manage Chronic Conditions
Make sure that you are not diabetic having high hypertension or high cholesterol levels before you travel. These factors are necessary to be kept in a good state in order to prevent or to slow down the process of the PVD.
Daily Management Tips
1. Monitor Symptoms
Make sure you pay attention to any modifications of your symptoms, such as throbbing and swelling, numbness, or a wound that does not heal quickly. If the symptoms you experience are additional or the existing problem aggravates, it is necessary to inform your doctor urgently.
2. Practice Good Foot Care
Check your feet regularly for any cuts, sores, or signs of infection. Keep your feet clean and moisturized, and wear well-fitting shoes to reduce the risk of foot problems that can lead to complications in PVD.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Carrying the extra weight overworks the heart muscles and stresses blood vessels, thereby increasing the chance of developing PVD. Additionally, a healthy diet and regular physical activity can help you maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of complications from PVD.
Conclusion
Doctors consider peripheral vascular disease a chronic illness in individuals. The effective condition management and intervention services, with the required monitoring, can make the patients lead a fulfilling life while reducing the severity of PVD in their routine. Through healthy lifestyle choices, seeking medical care at the right time, and being proactive about their vascular health, individuals can decrease the likelihood of complications, and ultimately, they will also be able to enhance their overall well-being.