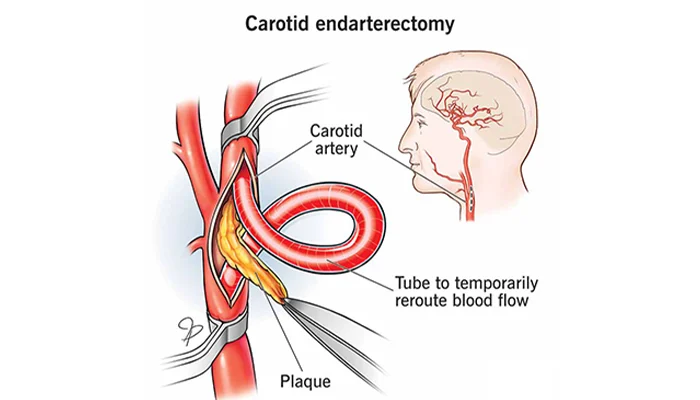
Frequently Asked Questions About Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Why Is CABG Performed?
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is considered to be a therapeutic intervention procedure that requires being performed due to the development of CAD that causes chest pain and shortness of breath that can cause a heart attack. It is mostly applied when all the other treatments including medications and lifestyle modifications are no longer efficient in curing the particular condition.
What Is the Time Required for Complete Recovery from CABG?
Full recovery may require 10-12 weeks. It should be noted that during this period individuals are required to adhere to the lifestyle recommendations and closely follow cardiac care through participation in the cardiac rehabilitation and follow other physician’s recommendations.
Is CABG a Cure for Heart Disease?
It exactly relieves the arterial blockage to ensure the blood flow to heart muscle but it does not reverse the coronary artery disease. Continued lifestyle change and medication are the primary interventions to manage the condition further.
Will I Need Another CABG in the Future?
Graft lifespan can vary. It is always essential to maintain a diet that will make the grafts last long without getting too many requests for reoperation. Contact with a healthcare provider is necessary to evaluate and sustain heart conditions.
When Can I Resume Work Post-CABG?
Complete recovery takes 6 to 8 weeks; most patients can return to work during this time. Nevertheless, those working activities that involve physical activities must recover longer to ensure they can be performed safely.
Statistics on Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
CABG cannot be described from just the numbers of its prevalence and its successes in treating heart disease. Here are some key statistics:
Prevalence
CABG is indeed one of the most widely performed heart operations worldwide. On the American side, about 200,000 CABG procedures are performed every year.
Success Rates
CABG is, however, a relatively safe procedure. 95-98% of the patients treated with the procedure gain satisfactory relief in their symptoms and improved circulation in the heart muscle. Improvements have also been achieved in surgical technologies and post-surgical care, leading to increased long-term survival rates.
Survival Rates
Research reveals that the 5-year survival rate for CABG patients reach up to 90% and a similar survival rate of about 80% is observed in 10 years. The rates may depend on whether you are old, young or if you have any other medical issue.
Complication Rates
This procedure is low risk also compared to years ago. Now the risk of having a life-threatening complication such as heart attack, stroke or death is less than 2-3%. The risk is higher in the elderly and those of cardiovascular disease.
Quality of Life Improvements
In addition, CABG even improves the quality of life for some patients by relieving symptoms and allowing them to return to physical ability, which they had not experienced for years. About 85-90% of patients experience relief from angina and other symptoms after the surgery.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Effective Management and Recovery
Case Study 1: John’s Journey to Heart Health
John was a 58-year-old businessman suffering with congestive heart failure and also experiences chest pain and breathlessness. He spends one week in ICU and three more at the hospital after having a triple bypass surgery and he went to cardiac rehab. He began to eat healthily and to exercise. Six months after the surgeries, John had no chest pain or breathlessness, and these changes indicated that he benefited from surgery, medicine, and a change of lifestyle.
Case Study 2: Maria’s Path to Recovery
Maria was a 65-year-old teacher who suffered from high blood pressure and high cholesterol for long and severe blockages were there. She had a quadruple bypass surgery that was spent 10 days in the hospital. It is during the cardiac rehab sessions that she adopted the Mediterranean diet, exercised and quit smoking. One year after the accident, Maria recovered well and obeyed the instructions of the program well; her heart was functioning normally, and her blood pressure and cholesterol levels were stabilized and even reduced.
Conclusion
CABG is also life-saving for patients suffering from severe coronary artery disease because it helps the coronary artery supply blood to the heart more effectively and relieves symptoms like chest pain and shortness of breath. There are various limitations of CABG, as it only serves to reduce the chances of heart attacks but does not address heart disease. Heart health treatment entails changing life habits, regularly taking medications, and continuous care. A high success and survival rate highlight its effectiveness, while cases like John and Maria’s aptly demonstrate its efficacy when practiced alongside other rehabilitations and lifestyle changes.