What Is Cardiac Ablation?
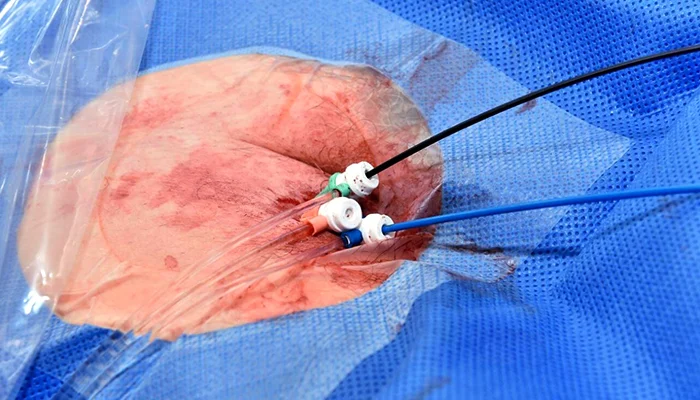
A cardiac ablation is a medical procedure that treats irregular heartbeats, known as arrhythmias, by destroying electrically damaged tissues of the heart. During the ablation process, healthcare providers guide a catheter into the blood vessels. They use a source of energy to target specific sites responsible for causing the abnormal beats. This energy either kills or changes abnormal tissue, thus returning the heart’s rhythm to normal.
Common Types of Arrhythmias

Depending on the individual problem, arrhythmias may be differentiated into patterns that affect different regions of the heart. Here are some common examples:
1. Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Atrial fibrillation is the state in which the heart’s (upper chambers) may beat out the pattern and vibrate instead of contracting normally. This will affect your heart rate, which will be irregular and, at times, quite rapid. Additionally, it is very common for people living with atrial fibrillation to experience abnormal heartbeat rhythms, shortness of breath, or weakness.
2. Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
VT, on the other hand, is an abnormal type of arrhythmia in which ventricles or lower chambers of the heart rapidly beat. Lack of proper atrioventricular sync can provoke such severe symptoms as the heart’s alternating rhythm and blood volume unevenness. Consequently, VT effects may evoke different sensations, like blacking out, chest pain, and fainting.
3. Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
SVT or supraventricular tachycardia can be defined as an abnormally elevated heart rate, which can either occur in the atrium or in an atrioventricular node, which is found above the ventricles. This type of stress tends to be represented by the accelerated rate of the heart beat, and is associated with symptoms like palpitations, breathlessness, and chest pain. The episodes of SVT may come suddenly and, after intervention, can lead spontaneously or can be cured.
Symptoms of Arrhythmias
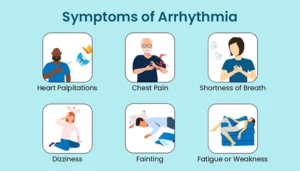
1. Palpitations
Palpitations are perceptions of the heart that may feel like fluttering, pounding, and racing. Frequently, patients mention the sensation of their heart jumping or experiencing an alteration in rhythm. Additionally, irregular heartbeat may manifest as occasional or continuous palpitations, often accompanied by feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness.
2. Chest Discomfort
A chest discomfort or pain can be a manifestation of arrhythmias, especially in the case of atrial fibrillation or ventricular arrhythmias. Patients could suffer from such symptoms as pain, pressure, or a feeling of tightness in the chest. This feeling might be considered to be like a heart attack’s, and your doctor should examine it as soon as possible.
3. Shortness of Breath
Arrhythmias interfere with the efficiency of the heart to pump blood and oxygen, thus, oxygen delivery to the different parts of the body is reduced. A consequence might therefore be the development of breathlessness or difficulty breathing, predominantly in cases of physical exertion or in supine position. Suddenly, a patient may be feeling like they are unable to catch a breath, and their breathing becomes very intense.
4. Fatigue
Chronic fatigue without valid reasons or continuous tiredness usually occurs in those diagnosed with arrhythmia. Due to irregular movement and disorganized strokes, the heart fails to pump blood efficiently, reducing its flow to vital organs and muscles. As a result, patients may experience fatigue, weakness, or a general inability to participate in normal activities.
5. Dizziness or Fainting
Arrhythmias can lead to a lack of blood flow to the brain, which results in brain function malfunction, such as dizziness, lightheadedness, and syncope. These symptoms often erupt without warning and are commonly induced by a change in position, largely due to standing up quicker. When fainting happens, the healthcare provider should try to investigate the cause or triggers of the symptoms without delay.
6. Fluttering Sensation in the Neck
Some individuals may experience a fluttering sensation in the neck during arrhythmias, particularly atrial fibrillation. This sensation, known as a pulsation, occurs due to irregular blood flow caused by abnormal heart rhythms. Patients may also notice visible pulsations or throbbing in the neck region.
Risks Associated with Untreated Arrhythmias
Leaving arrhythmias untreated can lead to significant health problems, which are as follows:
1. Stroke
The clots may be formed by atrial fibrillation, the arrhythmia. Consequently, these clots may travel to the brain and cause strokes, potentially resulting in death or permanent damage.
2. Failure
The presence of arrhythmias impairs the heart’s ability to pump. As a result, this can lead to heart failure, where the blood flow may not be sufficient to meet the body’s oxygen and nutrient needs.
3. Cardiac Arrest
The rhythm disturbance originating from lower heart chambers is the most potent to initiate sudden cardiac arrest. Sudden cardiac arrest occurs when the heart stops unexpectedly, posing a fatal emergency where immediate medical intervention is crucial to save the patient’s life.
4. Worsening Heart Conditions
Arrhythmias left uncontrolled may develop into more severe health issues, such as coronary artery disease and so on, which gradually endanger patients’ lives.
Identifying arrhythmias early, and treating them strongly, is the best way to reduce mortality, and improve living conditions for the individuals.
The Cardiac Ablation Procedure

Cardiac ablation is a procedure to cure abnormality of electrical routes by means of targeting problematic routes in the heart.
Preparation
To qualify for the procedure, healthcare providers conduct a thorough evaluation of patients, including reviewing their medical history, performing a physical examination, and conducting diagnostic tests such as ECG and echocardiogram. These tests identify the type and severity of the arrhythmia experienced. During the treatment, patients might get sedation and have electrodes placed on their chest to watch all the heart activity on a continuous basis.
Catheter Insertion
Following the completion of all pre-procedural preparations, the next step would be inserting the catheter. Healthcare providers introduce a thin, flexible catheter into a blood vessel, typically in the groin area, under fluoroscopy. They carefully guide the catheter to the heart with precision and care, utilizing fluoroscopy, an X-ray technique that allows the healthcare team to monitor the position of the catheter in real time.
Mapping and Ablation
By doing that, it enables the doctor to conclude what certain heart parts are the cause of the cardiac arrhythmia. This then identifies the target locations, and the catheter delivers energy to form a scar. The scar tissue introduce an energy barrier, thus stopping the abnormal electrical signals, most times successfully, and restoring the heart’s usual rhythm.
Monitoring and Assessment
The healthcare team closely controls the patient’s vital functions and heartbeat during the procedure through monitoring to guarantee safety and success.
Recovery
Healthcare providers monitor patients for several hours after the ablation procedure to ensure there are no immediate complications. Once patients are stable, providers typically discharge them home with instructions for recovery.
Towards a Healthier Heart
Arrhythmia ablation emerges as a suitable treatment modality in the cases of patients who do not react satisfactorily to drug therapy or other conservative treatments. Moreover, the process of ablation corrects abnormal electrical pathways, restoring a normal heart rhythm and improving the quality of life for the patients affected. If you experience symptoms potentially connected with arrhythmias, such as palpitations, chest discomfort, or unexplained loss of consciousness, it is crucial to promptly visit your doctor or a heart specialist. Your healthcare provider may recommend different treatment options, including cardiac ablation, and also assist you in making informed decisions about your cardiovascular health.