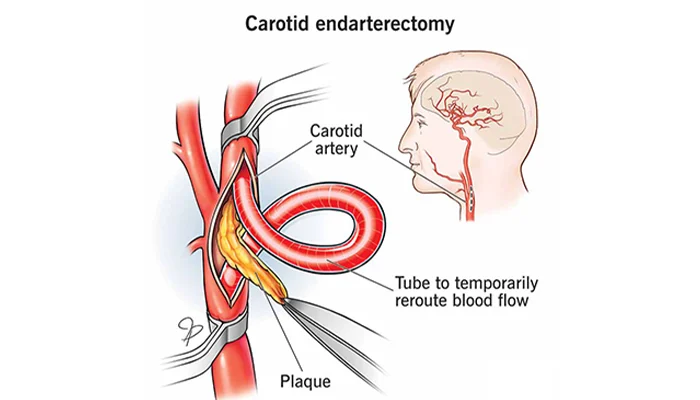
FAQs About Carotid Endarterectomy
Q1. What Kind of Recovery Is to Be Expected After Carotid Endarterectomy?
It involves keeping the affected person within the hospital for one or two days, typically known as convalescence. Moreover, some effects the patients may experience are neck tenderness and enlargement after the procedures. The period of convalescence may extend; furthermore, the specific time may range from weeks, and the patient should avoid lifting heavy objects and any activity that may cause him or her strain.
Q2. Can Lifestyle Changes Help After the Surgery?
However, one can reasonably agree that changes are necessary in someone’s life. In order to avoid similar obstruction and decrease the risk of a stroke one might make changes to his/her life style that would include eating a healthy diet, exercising and not smoking. Additionally, one has to undergo checkups to manage the blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Q3. What Are the Risks of Carotid Endarterectomy?
Similar to any surgery intervention, carotid endarterectomy carries certain risks; the following are the most common risks: Cerebral infarction, coronary heart failure, peripheral nerve injury, infection, and hemorrhage. However, when it comes to the surgery then, it is better not to look at these aspects of the result as the best way to live without a big-scale stroke is better than to have it.
Q4. How Effective Is Carotid Endarterectomy in Preventing Strokes?
This intervention commonly known as carotid endarterectomy is among the most effective in minimizing the risks of stroke among the patients with severe carotid artery disease. However, research has also indicated that it is effective in preventing stroke in patients with early signs of the disease.
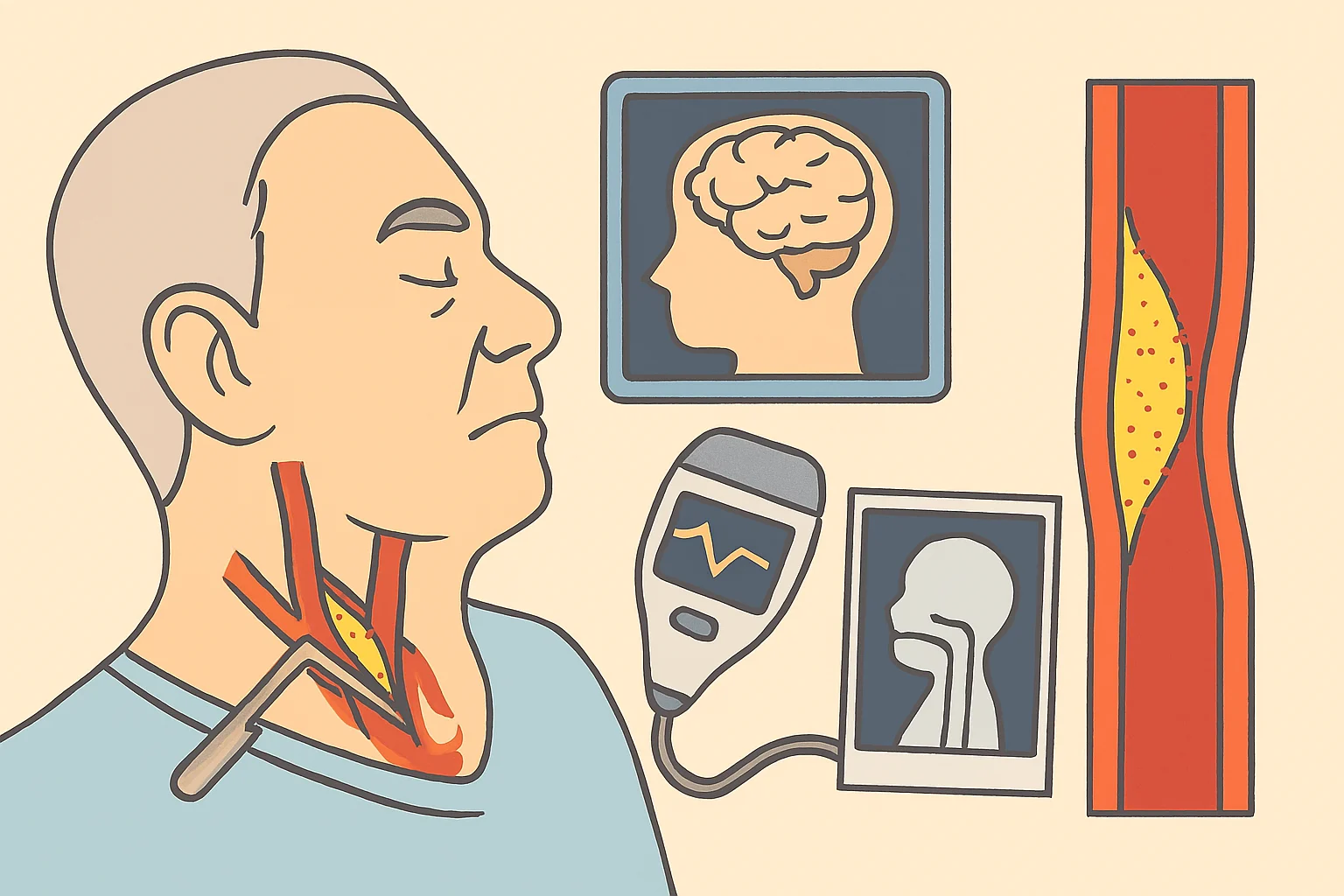
Q5. Who Needs a Carotid Endarterectomy?
Surgeons typically perform this surgery on patients whose carotid arteries are over 70% blocked. They also consider previous warning signs, such as a mini-stroke.
Statistics on Carotid Endarterectomy
- Carotid artery disorder is an international clinical condition that affects thousands and millions of people and is one of the prominent causes of stroke. Additionally, about 400,000 individuals in the United States of America are affected annually.
- Carotid endarterectomy helps to reduce the risk of stroke by 50 percent in patients who have essential stenosis of the carotid arteries. Doctors have observed that this procedure effectively reduces the risk of stroke in such patients.
- Complications like stroke or even death from the surgery are not typical. However, competent surgeons typically encounter complication rates ranging between one and three percent during the surgery. Moreover, this risk is much lower than the risk of stroke without surgery for those with severe blockages.
- Most patients recover well from carotid endarterectomy; typically, they stay in the hospital for one to two days and achieve full recovery within a few weeks. Many patients experience a significant reduction in the risk of stroke and an overall improvement in health.
Case Studies of Carotid Endarterectomy
Here are two success stories that show effective management and recovery:
Case Study 1: John’s Journey to Stroke Prevention
John, a sixty-eight-year-old retired trainer, had mini-strokes and a 75% blockage within the proper carotid artery. Later, he had carotid endarterectomy and this is the surgery that actually removes the blockage. As a result, he was able to recover swiftly and changed his lifestyle, thereby not only preventing him from having a severe stroke but also improving his health.
Case Study 2: Maria’s Road to Recovery
Maria, an accountant aged 62, had increased cholesterol and high blood pressure. After the physical examination, the medical professional decided that the left carotid artery was narrowed by 80%. Therefore, she was subjected to a carotid endarterectomy. With a smooth recovery, Maria managed her health through medication, exercise, and a support group. Consequently, her doctor praised her progress and reduced stroke risk.
Conclusion
Carotid endarterectomy is performed when there is severe carotid artery disease, and the surgery is used as a preventive measure against stroke. Knowledge through FAQs, statistics, and success stories aids informed decisions. Additionally, these stories of John and Maria are evidence that the procedure works and that early initiation of the health management plan is crucial. Dietary modifications, drug therapy, and periodic follow-up examinations are essential in preventing this condition. Additionally, they contribute to improving quality of life.