Overview of Coronary Artery Disease
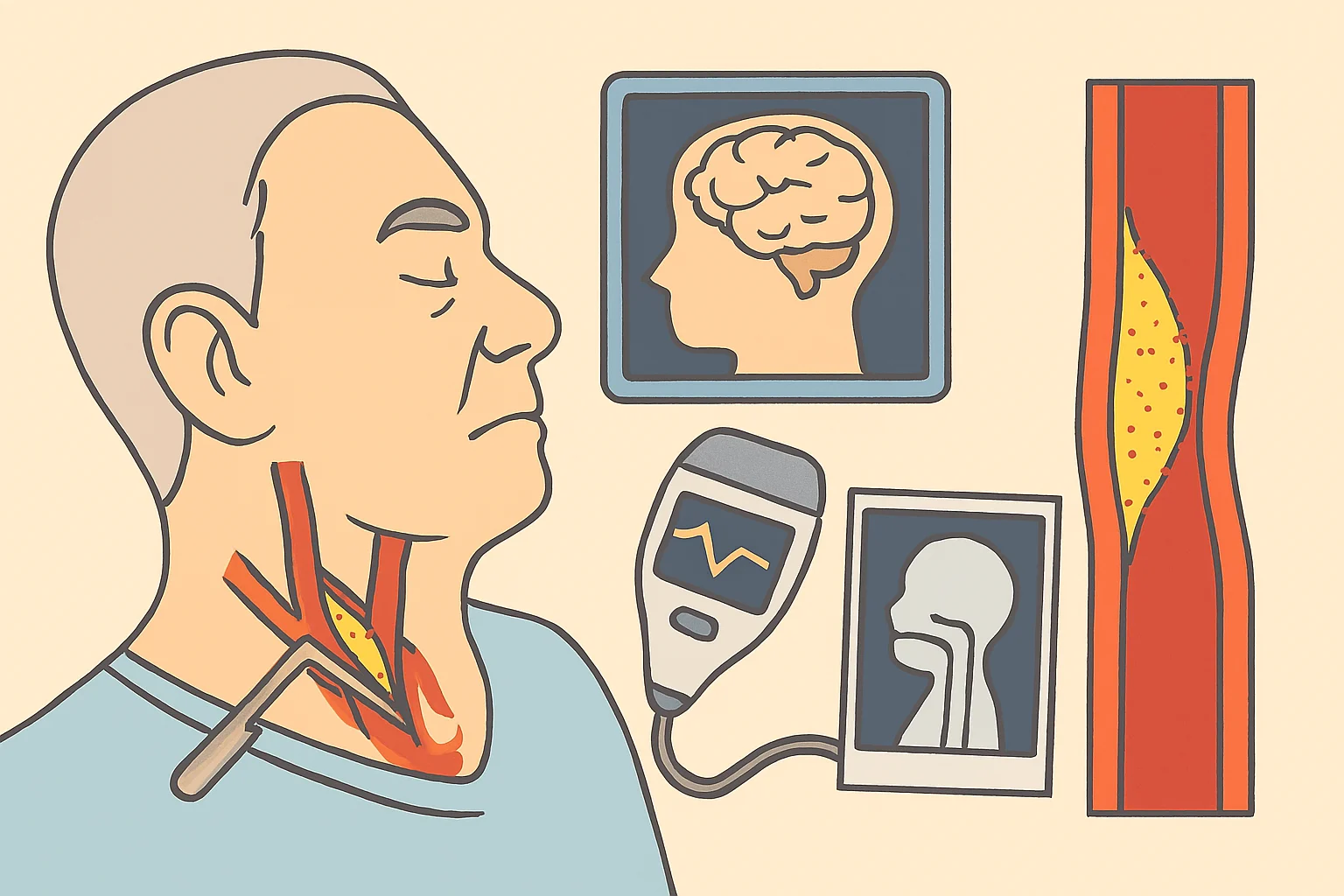
CAD is the most widespread type of cardiovascular disease, as well as a leading cause of death in the world. CAD stands for coronary artery disease. Coronary arteries, which nourish the heart, become blocked or narrowed by a buildup of cholesterol and fatty deposits in this condition. Fats, cholesterols, calcium, and other substances present in blood form plaque. The earliest stage of arteriosclerosis is when plaque deposits begin to form along the artery walls negating the easy flow of blood into the heart. This may result in chest pain and shortness of breath and other related symptoms. If the plaque bursts, a clot may form. This clot can lead to a complete blockage of blood flow, known as a heart attack.
CAD can have a serious effect on your life and lead to elementary and often hazardous task. CAD is not something that one wakes up with one day. Hence, learning the causes, symptoms, and treatment methods is crucial. It frequently spans years and sometimes decades, and the primary manifestations may be absent at onset. Hence, as the disease state progresses the manifestations of Tuberculosis become worse.
Importance and Prevalence of CABG
CABG remains mandatory for patients with severe CAD. These patients may require additional treatments due to the ineffectiveness of percutaneous interventions. Alternatively, they may undergo other minimally invasive procedures such as angioplasty. Another treatment option is angioplasty, which uses a narrow balloon to open an artery blocked by blood clots. CABG involves grafting a suitable artery or vein from the body or harvested from another part of the body. This creates an alternate route for blood flow when an artery becomes blocked. This goes a long way in helping to regain normal blood flow within the heart muscles.
CABG is not a rare surgery; in fact, it is among the most performed surgical operations around the world. Every year, surgeons in the United States perform nearly 200,000 CABG surgeries. It has been established that surgery results in increased survival for advanced CAD patients who opt for it. Surgery also alleviates symptoms associated with the condition. In particular this is useful for patients with more than one artery blocked, or severe blockages in one or more large arteries.
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease Leading to CABG
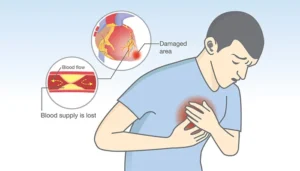
In order to arrive at an early diagnosis and consequently manage CAD, one has to be in a position to identify the diseases symptoms. Symptoms of LE can be different in each patient, as well as their intensity which may be mild or severe. Here are the common symptoms of CAD that may lead to the need for CABG:
1. Chest Pain (Angina)
Stable Angina
People experience this chest pain regularly during exercise or emotional stress. Common symptoms of CAD include mild discomfort that lasts for a few minutes after exertion and is relieved by rest or medication. This discomfort may feel like heaviness, squeezing, or simply a sensation of pressure in the chest. It also affects the limbs, arms, neck, lower jaw and back.
Unstable Angina
This is more severe and difficult to determine on how it would go. This can happen even while sitting or lying down. It triggers with less exertion and can last longer than stable angina. Despite not requiring complete bed rest or medical treatment, the mentioned condition can predict an impending heart attack. It requires medical attention as soon as possible.
2. Shortness of Breath
Another indication of CAD is shortness of breath or dyspnea, which a person may experience during physical exertion or everyday activities. It can also occur when patients are at complete rest. This may occur when the heart is not supplied with adequate oxygenated blood. As a result, it may struggle to perform its pumping function effectively. Shortness of breath is a symptom of a disease or disorder characterized by the perception of labored or inadequate breathing. It may occur especially during physical activity when breathing should normally be comfortable. Simple exercises like climbing up the stairs may become difficult and you may feel panting after doing so.
3. Fatigue
Fatigue resulting from CAD is the feeling of being tired or weak that does not disappear with rest or sleep. This type of fatigue is often less obvious but illustrates the fact that the heart is not pumping blood as it should. That is why your body tissues, cells, and organs fail to get enough oxygen supply. This causes them to function constantly at optimal exhaustion. It may be possible to feel tired and panting after a routine activity like walking a few blocks or doing some minor chores at home. This can severely hamper the daily living of an individual.
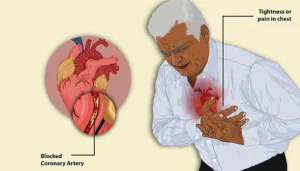
4. Heart Attack
The ultimate stage of CAD is a heart attack, or myocardial infarction. A blockage in a coronary artery shuts off the blood supply to a part of the heart. The common signs of a heart attack include chest discomfort, which may feel like a torment or squeezing sensation. The discomfort may feel heavy, throb with pain, or radiate to the arms, neck, jaw, or back. Other symptoms can include breathing difficulties or shortness of breath, extreme sweating or pale skin, vomiting, and dizziness or actual passing out. This is a medical emergency condition that demands timely intervention. The goal is to re-establish blood circulation in the heart and avert the risk of any form of heart damage.
5. Dizziness or Lightheadedness
Less blood circulation in the head leads to dizziness or fainting; you may feel dizzy and unbalanced. This is because the heart is not pumping enough blood supply to circulate round the body and specifically to the head. You may get a sense as though the room is rotating. Other times, you may experience dizziness that causes a feeling of instability, which might lead to a fall or even a feeling of passing out. This symptom can be problematic, as it would render a person unable to go about their daily tasks without risking their lives. It could also be an indication of severe heart complications that would necessitate immediate medical intervention.
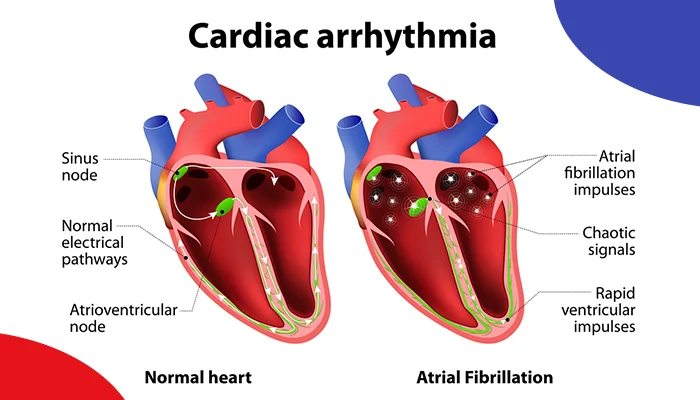
6. Palpitations
Palpitations are experiences that tell you that your heart is beating in a strange way. It may feel too fast or with hard force. They can develop when the heart attempts to increase the manufacture of blood to meet the need created by blocked or narrowed arteries. This can lead to an irregularity of heartbeat. Among the areas where you might palpate them include the chest, throat, or neck; and this often comes hand in hand with anxiety or discomfort. Although some people may experience palpitations at times that are non serious, if one regularly or experiences severe palpitations, they need to seek medical assistance.
7. Swelling
Edema is a condition characterized by puffiness or swelling of the legs, ankles, and feet. Compromised heart functionality may attribute to it, resulting in inadequate blood circulation. This is the case because the lower rate of blood circulation leads to leakage of fluid from a vessel into tissues. The affected area might look puffy or taut. You may even be able to indent the area when you apply pressure. It can therefore cause discomfort and may make it challenging to walk or to wear shoes and socks. Swelling is an indication that heart function is impaired or shutdown which requires medical intervention.
Detailed Examination of CABG Procedure
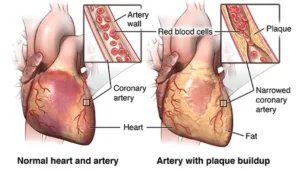
A cardiac surgeon typically performs CABG, which is best defined as a complex and often highly invasive procedure. During the surgery, the patient undergoes general anesthesia, ensuring they feel nothing throughout the entire operation procedure. Here are the main steps involved in CABG:
Preparation
Apart from blood tests, healthcare providers perform imaging studies to prepare you for coronary angiography before conducting surgery. These tests help determine your general health condition and the extent of arterial blockage. Your healthcare team will also give you instructions, such as refraining from some medications and possibly avoiding eating before the surgery.
Harvesting the Graft
The surgeon is likely to make incisions to obtain a healthy blood vessel which will be used as a graft. The vegetables most often used for this purpose are internal mammary artery that is harvested from the chest, saphenous vein from the leg, and the radial artery from the arm. The selection of the type of vessel to use depends on the position of the blockage and the wellbeing of the patient.
Performing the Bypass
The actual surgery entails an operation in which the surgeon makes an incision across the sternum. This results in the division of the chest in a bid to access the heart. These may include stopping the heart temporarily through the help of an apparatus known as the heart-lung machine. This machine not only assists in the heart’s function of pumping blood but also supports the lungs in carrying out respiration. One other method is undergoing this surgery on the patient’s functioning heart is the off-pump CABG. The surgeon then connects one part of the graft to an area of the artery that is above the blockage then at one other point below the blockage to ensure that there is a passage way for the blood in the artery.
Closing the Incision
After ensuring healthy grafts and restoring circulation, the surgeon consolidates the sternum and closes the chest opening. You will then be taken to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) primarily to recover from anesthesia.
Postoperative Recovery and Rehabilitation

Recovering from CABG involves several processes that, though achievable within a short period, require utmost concentration and meticulous care to enhance the chances of success.
Immediate Postoperative Care
After the surgery, medical staff will move you to the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) for intensive supervision, typically lasting about 24 to 48 hours. After that, the medical staff will monitor your condition and changes concerning the vital signs and pain perception and look after the postoperative wounds. It is important that you ensure that your heart is healthy during this time and that there are no complications that are sắp to occur.
Hospitalization
Depending on your recovery progress, you may be hospitalized for five to seven days. Over this time, you will get out of bed, and gently beginning to walk around or do some very light exercises so that the blood starts circulating well without offending your pelvic area; this is because if not well managed, blood clots may form. The medical officers recommending diet and nutritional tips and also on how to handle surgical wounds and pains at home.
Rehabilitation
Cardiac rehabilitation is part of the recovery phase that needs to be incorporate in the treatment process. These consist of cardiac rehabilitation that entails exercise, counseling regarding healthy lifestyle and practical support for those struggling with severe emotions. Cardiac rehabilitation is a process that reaches the patient’s physical, mental, social, and spiritual well-being and seeks to assist him or her to return to a healthy lifestyle while avoiding further heart issues. It also encompasses other practices including; taking multiple doses of recommended healthy foods to support the heart, avoiding smoking, accepting stress and other medications as advised.