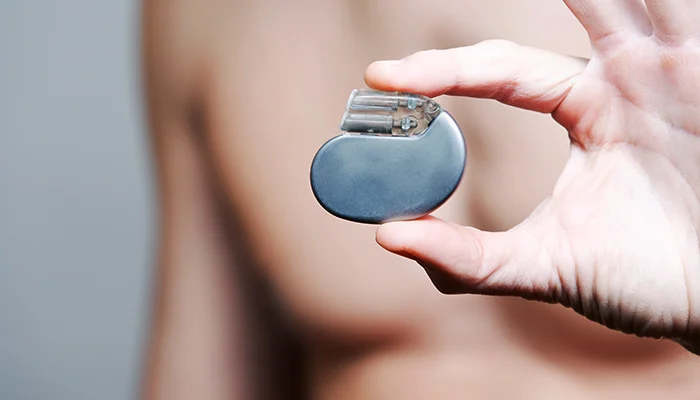
Why is There a Need for Pacemakers?

Pacemakers serve as little assisting hands for hearts struggling with keeping one rhythm. When someone feels dizzy or faint due to an irregular heart rhythm, pacemakers are introduced. These devices help bring the heart rhythm back on track. Here are common causes of pacemaker utilization:
1. Sinus Node Dysfunction (Sick Sinus Syndrome)
The sinus node, which serves as the heart’s natural pacemaker, can sometimes fail. This failure may manifest as arrhythmias characterized by a too-fast, too-slow, or inconsistent heartbeat. This symptom can easily result in feeling light-headed and even fainting. An artificial pacemaker is designed to send electrical pulses to the heart. These pulses help prevent all irregularities of the rhythm.
2. Heart Block
This occurs when there is a delay or interference in electrical signals between chambers within the heart, causing slow or spontaneous pulse rates. This will cause fainting, dizziness, and fatigue. A pacemaker is an electronic device that replaces lacking nodal tissue. It bridges the communication gap between the heart chambers, maintaining a steady and regular heart rhythm.
3. Bradycardia
Bradycardia is essentially a natural condition where the heart cannot pump sufficient levels of blood. This can result in symptoms such as dizziness, fainting, fatigue, and shortness of breath. Getting this disorder might be as a result of aging, taking medications or because one is suffering from a heart condition. Normally, pacemakers are implanted in the body to help maintain a smooth rate of heartbeats. They supply electrical impulses that guide the heart muscles to beat when the heartbeat is too slow.
4. Tachy-Brady Syndrome
In the state, the heart has sudden and frequent episodes of beating wildly and then without any rhythm. These sudden things that happen within a fraction of a second can probably make you feel so unwell, either with symptoms of dizziness or with your heart pumping too fast. Pacemakers help to pace these irregular rhythms of heart, making them regular and good enough so that no such difficulties emerge.
5. Atrial Fibrillation with Bradycardia
Atrial fibrillation involves the heart’s top chambers beating in an irregular pattern which then results in occurrence of symptoms such as palpitations or shortness of breath. In such cases the heart doesn`t always meet the demands of the body (bradycardia). Pacemakers can regulate the heartbeat. They also ensure that it remains at a normal pace, especially in cases of atrial fibrillation.
6. Heart Failure
Certain form of heart failure, especially the one that accompanies arrhythmias, can be treated with lining up of a pacemaker. The cardiac failure happens when heart muscle is unable to pump blood efficiently which leads to breathlessness, feeling tired and accumulation of fluid in lower parts of the body. Permanent pacemakers control the heart’s contractions, improving its overall function. They troubleshoot the main symptoms experienced by these patients and enhance their quality of life.
How Do Doctors Diagnose the Need for a Pacemaker?

Now that we have uncovered the reasons leading people to have pacemakers installed. Let’s find out how healthcare professionals determine their necessity. Techniques of diagnosis are crucial for detecting cardiovascular health status. They also guide doctors in managing their patients appropriately.
1. Electrocardiogram (ECG)
The doctors also use the ECG, or ECG, in cardiology. This test involves recording the electrical activities of the heart. Patients lie down, and healthcare providers patch small stickers (electrodes) on their chest, arms, and torso. These electrodes pick up and detect the electrical signals from the heart. They create a picture that portrays the regular rhythm of the heart. ECG shows if there are unnatural heart rhythms, for instance, some heartbeats are too fast or too slow. And it helps doctors to diagnose exact cardiovascular problems.
2. Holter Monitoring
The Holter monitor is a portable device which is the wearer which records the heart’s rhythm each two hours over 24-48 hours long. Patients wear the monitor as a small box or pouch on either the waist or neck. Wires are attached to the patient’s chest and linked to electrodes. The monitor represents in sequential form the heart rate during patient’s everyday habits. A Holter monitor can grab the irregular heart arrhythmias that a wearable device perhaps would skip to miss if exposed to a short-term ECG. This enables a consistent screening of the patient for any evident pattern or heart rhythm disturbance.
3. Echocardiogram
This is a kind of image test that produces pictures of how the structure and functioning of the heart work with the use of audio waves. The healthcare provider places the transducer device on top of the chest. This, in turn, reflect the soundwaves that skim off the heart and in future leads the formation of images on a screen. They reveal a round structure of the heart (the size is being highlighted as well) as well as blood flow from one chamber to another. By using an echocardiography, doctors can see more clearly the abnormalities inside the heart which may cause irregular heart beats, these disorders leave vital signs for diagnosis and treatment planning.
4. Tilt Table Test
The tilt table test is one of those diagnostic tests that used to detect the reason for fainting spells or syncope. The test is conducted while healthcare providers position the patients lying down on a specially designed table, noting the time. Then, healthcare providers gradually tilt the table upright while monitoring the patient’s heart rate and blood pressure. The tilt mimics the change in position that can trigger fainting episodes. The test serves the doctors in establishing if fainting arises due to either heart rate or blood pressure fluctuatation, and they can quickly identify the underlying cause.
5. Event Recorder
Patients can use event recorders to preserve their heart’s rhythm when they have symptoms. If individuals encounter palpitations, they simply carry and trigger them. During these periods, healthcare providers record what is happening inside someone’s heart on this recorder. It is a version of a recorder that helps professionals in saving instances of unusual heart rate that might assist in determining and forming a treatment solution.
6. Electrophysiology Study (EPS)
An electrophysiology study (EPS), a diagnostic tool, comprises several elements aimed at providing a detailed anatomical picture of the heart’s electrical activity. Thin, flexible tubes called catheters are guided into the heart through the blood vessels during this procedure. These catheters monitor the heart’s electrical signals and can at times introduce these arrhythmias to map out where the cause of the problem is among the abnormal rhythms. EPS helps doctors identify arrhythmias’ specific type and location, guiding treatment decisions and interventions.
7. Stress Testing
Stress testing can be performed as heart activity is being tracked while an individual is performing physical activity like walking on the treadmill. It is used to diagnose heart diseases as a result of an improvement in the heart’s response. This test is done for detecting both arterial disease and heart rhythm under emotional stress. It is one of the significant tools for measuring heart’s function as well as guiding treatment to be taken. Through the stress testing process health centers gain the critical understanding of heart condition and overall cardiovascular functionality.
These diagnostic tools are essential for assessing heart conditions. They enhance treatment outcomes and the quality of life when a pacemaker implantation is necessary.
Understanding the Necessity of Pacemaker Implantation
In other words, heart pacemaker implantation represents a course of healing for people who experience disintegration of the electrical system within the heart. These systems, which restore rhythm and stability to the body, enable patients to lead active and happy lives if they are suffering from heart blockages, bradycardia, or arrhythmia.
Physicians practice accurate investigation of the health of the heart when they perform techniques such as electrocardiography, Holter monitoring, echocardiography and tilt table testing. Depending on the findings these physicians will recommend the need to fit pacemakers. They provide the healthcare practitioners with the opportunity to engage in personalized medicine that allows for treatment plans adapted to patient-related needs which in turn leads to better results and better quality of life.
So, the next time you hear about someone receiving a pacemaker, remember the intricate process of diagnosis and the critical role these devices play in restoring and maintaining heart health. It’s not just about fixing a problem; it’s about safeguarding the rhythm of life itself.