Understanding Carotid Artery Disease
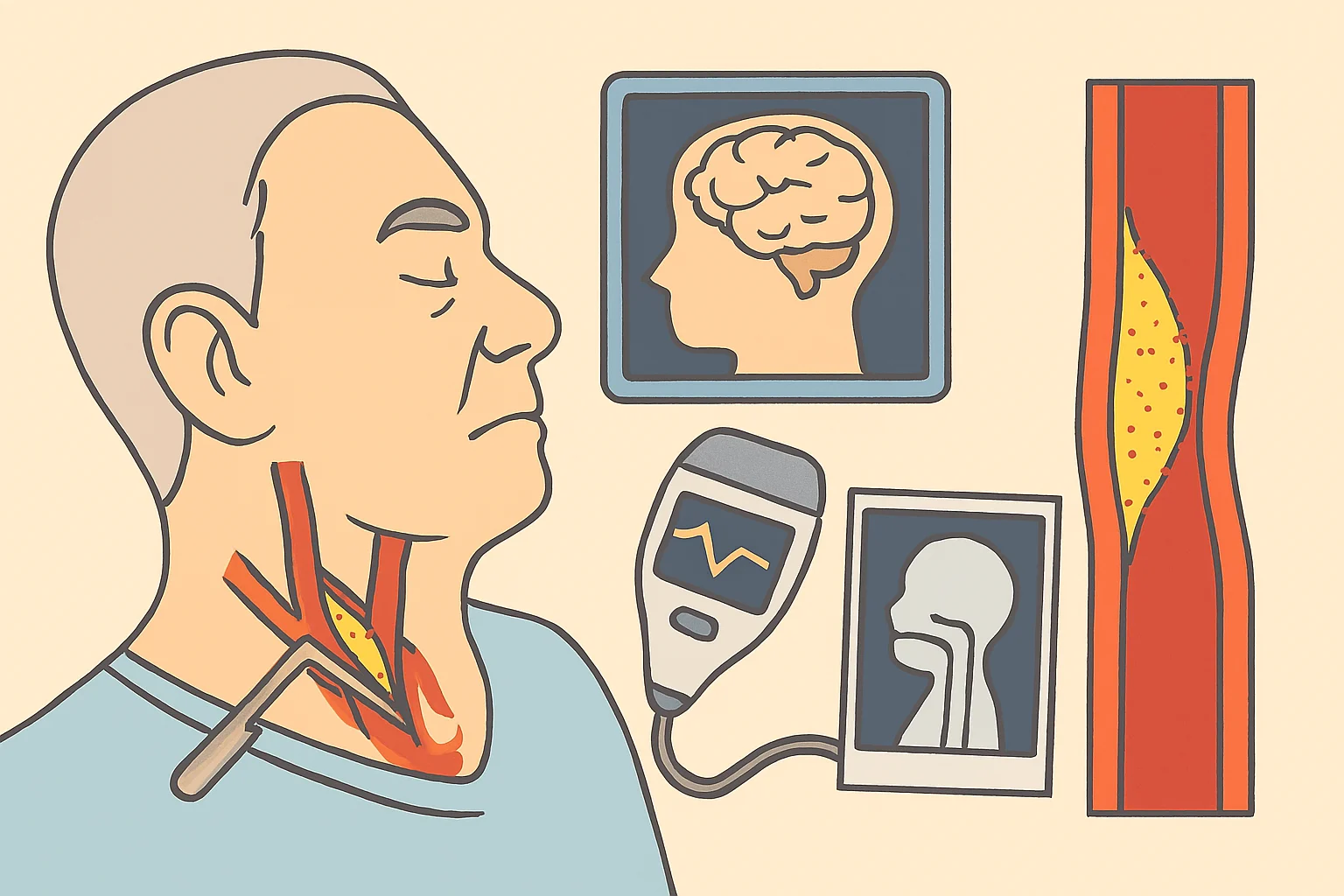
Carotid artery disease or carotid stenosis is the constriction of the internal lining of the carotid arteries. This narrowing is due to the formation of plaques, cholesterol, fatty materials, waste products, calcium, fibrin, etc Atherosclerosis is dangerous because it leads to the blockage or constriction of the arteries and may lead to the following complications.
The organ that is at risk of developing ischemia when the carotid arteries are stenosed or occluded is the brain. This condition makes TIAs and stroke more likely because the organ needs oxygenated blood for its operations. A TIA is commonly referred to as a ‘mini stroke,’ which is a temporary ischemic attack in which the affected person exhibits some of the symptoms of a stroke.
Prevalence and Significance
Another not rare pathology is carotid artery disease, often identified in elderly patients. Surprisingly, the incidence of carotid artery stenosis is comparatively high. According to statistics from the American Heart Association, about 5 percent of the adults in United States of America, 65 years and older years and older have carotid artery stenosis. This condition is marked by high blood pressure and high levels of cholesterol in the blood serum. Other causes include tobacco use, diabetics or history of it, past or present obesity and physical inactivity.
Therefore, it becomes crucial to address carotid artery disease by analyzing changes in lifestyle and medication. In some circumstances, doctors recommend carotid endarterectomy to reduce the risk of stroke.
What is a Carotid Endarterectomy?
Surgeons perform carotid endarterectomy to remove plaques that have developed in the carotid arteries. This procedure helps improve blood flow to the brain and reduces the chances of a stroke. The specific details of the surgery involve cutting the skin on the anterior part of the neck. This enables the surgeon to access the carotid artery. The surgeon then proceeds to perform an angioplasty, enlarging the narrowed artery before removing the plaque. After removing the plaque, surgeons seal and repair the artery to restore normal blood circulation.
The foregoing procedure is comparatively safe for preventing strokes in individuals with severe carotid artery disease or those with a history of TIA or minor stroke. It is particularly beneficial for these groups of patients.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for Carotid Endarterectomy
Learning the symptoms of carotid artery disease is equally vital for people to take early appropriate measures. Here are some common signs that may indicate the presence of significant carotid artery disease. These signs could necessitate a carotid endarterectomy.
1. Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs)
It is also known by other names including TIA or mini-stroke. This condition, while separate from a stroke, only affects a certain area of the brain for several minutes up to several hours. These symptoms are characterized by the sudden onset of numbness or weakness in any part of the face, arm, or leg — especially on one side of the body. Individuals may also experience sharp difficulties in speaking, understanding, reading, writing, or recognizing pictures or learned materials. These symptoms can indicate a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or mini-stroke. For many years, these events were termed TIAs, indicating a warning sign that a major stroke is likely to occur. However, TIAs do not directly impact the brain.
2. Stroke
A stroke is a medical condition causing similar signs and symptoms as a TIA. Its effects can last for more than twenty minutes and may lead to more serious consequences. They also argued that early health care is appropriate to reduce harm to the brain tissues and other organisms. Our research findings reveal that detecting the signs and symptoms of post-stroke early is crucial. Patients should be taken to the doctor as soon as possible because early treatment yields better results. Delayed treatment may lead to less favorable outcomes.
3. Sudden Numbness or Weakness
Changes in vision or abnormal sensations may indicate that the carotid artery could be blocked. Symptoms such as diffuse or localized paralysis and dizziness can also suggest potential issues with the carotid artery. Additionally, severe headaches may indicate blockage in the carotid artery. This sign occurs because the region of the brain responsible for these functions lacks proper blood supply. Consequently, it cannot perform its duties as expected.
4. Trouble Speaking or Understanding Speech
Temporary slurred speech may occur due to poor circulation in the blood vessels in the areas of the brain that control language. This can also lead to the inability to understand what others are saying. This may present as dysarthria, characterized by an inability to speak clearly and difficulty in pronouncing words. It can also involve difficulty comprehending simple language and constructing meaningful sentences.
5. Vision Problems
Frequently, carotid artery disease is accompanied by blurry vision or the loss of vision in one or both eyes. It can also lead to the development of double vision. These signs arise from a poor supply of blood to the visual areas in the brain. They may result in loss of vision either temporarily or, if worsened, permanently.
6. Dizziness or Loss of Balance
Restricted or no blood circulation to the brain may lead to dizziness, vertigo, or difficulty in walking. Such signs can make the person feel more off balance. This can cause falls and injuries, especially among the aging population.
7. Severe Headache
A sudden sharp-and-severe headache may be the initial clinical manifestation of a stroke. The cause of the headache at this stage remains unclear. This type of headache is often different from the normal dull headache or migraine. Other neurological symptoms sometimes accompany it, necessitating the client to seek medical attention.
What to Expect During Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid endarterectomy is a treatment procedure performed to prevent the formation or buildup of plaques in carotid arteries. It aims to remove existing plaques and restore proper blood flow to the brain. Sometimes it is usually a local procedure and at other times general operation based on the kind of fracture involved. Here’s what you can expect during the procedure:
Preparation
It begins with the action preparing the patient which involves putting the patient to sleep since they will be in pain during the procedure. During the operation, medical staff closely monitor signs like pulse and blood pressure to ensure the overall well-being of the patient. This helps in maintaining optimal conditions and responding promptly to any changes during the procedure.
Incision
Then the surgeon anaesthetises the area and then goes on to surgically incise the neck by making an incision on the left side of the skin revealing the carotid artery. More emphasis should be placed on this section of the surgery because there is a high possibility of damaging nerves and other structures. Careful attention to this area ensures surgical precision and minimizes potential complications.
Plaque Removal
Once ready, the surgeon opens the artery and gently removes the plaques. This delicate process aims to restore proper blood flow and reduce the risk of complications. Sometimes, surgeons may temporarily place a small metal or plastic tube, known as a shunt, to divert blood away from the areas of the body undergoing cleaning. This technique ensures adequate blood flow and oxygenation during the surgical procedure. This assists to maintain the adequate blood provision to the brain during the procedure.
Closure
After this, the surgeon sutures the artery to make a seal and ensure that no blood escapes from the site. The surgeon sutures or staples the area of surgical intervention in the neck where stitches are used. Occasionally, they place a small tube beside the incision to drain any anticipated fluid buildup, leaving the tube open for drainage.
Recovery
At the end of the whole surgical process, the surgical team takes the patient to the recovery room for observation. In most cases, patients are discharged within the first two days of hospital stay provided there are no complications. Doctors and nurses always observe patients for signs of complications like bleeding and stroke and advise on what course of action should be taken.
The techniques involved in carotid endarterectomy include preparing the patient, performing the artery treatment, and observing the individual post-operation to ensure safe and effective recovery from the procedure.